It is very difficult to analyze the operation of even one cell of an animal organism for the reason
That in the framework of its microscopically small volume, a huge number of different processes are simultaneously taking place. This task can be simplified if we consider all the functions in turn. This approach is facilitated by the fact that between the cells of the body there is an effective distribution of labor - they are, to one degree or another, specialized in performing certain functions that are vital for the animal. Therefore, the body can be considered as a collection of specialized cells. Groups of equally specialized cells, such as those that form, for example, cartilage or muscles, are called TISSUES.
With all the variety of tissues, they can be reduced to four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous. In the lower multicellular animals, gastrointestinal cavities of them, for example, clear boundaries cannot yet be drawn between the individual types of tissues. In the process of evolution, further differentiation of tissues occurs.
Consider the above types of fabrics in more detail.
Epithelial tissue
Epithelium is the union of cells that cover the surface of the body and line its cavities. The cells in them are tightly pressed against each other, there is no intercellular substance between them, and blood vessels do not penetrate the epithelium. The epithelial cells themselves are based on a thin-fibered basement membrane, which is formed from extracellular material. Through its open position, the epithelium wears out quickly, but is able to recover due to the so-called cambial cells that are in it.
The functions of the epithelium are very diverse. Often they play a protective role, both in connection with their surface position, and due to the ability to secrete bacteriostatic substances. Often they contain receptor cells that perceive irritation. One of the important functions of the epithelium is the absorption and excretion of various substances. According to the functions, the structure of the epithelium also looks. Distinguish between integumentary and PROTECTIVE epithelium, epithelium containing receptors, absorption and excretory (excretory) epithelium.
According to their morphology, more precisely in the form of cells and the number of cell layers, the epithelium is divided into: PLANE, cubic and cylindrical (Fig. ....). If the epithelial cells are located in one layer (as in most invertebrate animals), the epithelium is called a single layer. In vertebrates, the epithelium is usually multilayered. Certain organs are built from individual types of epithelium. Strongly flattened epithelia line the blood and lymph vessels, body cavities and pulmonary alveoli, and the intestinal tract of almost these animals is characterized by a cylindrical epithelium.
Flagella or cilia are often located on the free surface of epithelial cells. Such ciliated epithelium in most higher stratified animals, except arthropods and roundworms.
Connective tissue
In connective tissues, a number of tissue forms are understood, connecting, on the one hand, various organs with each other, and on the other, forming a skeleton. This also includes blood cells. Connective tissues are characterized by a large amount of intercellular material, which consists of a structureless main substance and fibers. Of particular complexity are connective tissues in vertebrates, from which cartilage and bone skeleton are formed in them. Between connective tissues of various types there are transitional forms.
Distinguish between loose and dense connective tissue. The loose include fat, blood, lymph. To the dense - tendons, cartilage and bones, the structure of which we will meet later.
Muscle tissue
An integral feature of the vast majority of animals is mobility. This ability is based on the presence of muscle cells in animals that can contract in response to signals from the nervous system. Thanks to muscle tissue, various types of movements of the whole organism and its individual parts are possible. Muscle tissues also perform a supporting function, supporting the entire body and its individual organs in a certain position, and also protect internal organs (Fig. ....). We will learn more about their structure later.
NERVOUS FABRIC
The harmonious work of all parts of the animal’s body is due to the activity of specialized systems that control the functions of all organs. The main role in this is assigned to the nervous system, which consists of nervous tissue. Nerve tissue is able to perceive various irritations and conduct nerve signals to different parts of the body, which in a certain way react to them. It consists of special nerve cells, or neurons, which have a different number of processes, and the structure of which we will also meet later.
BODIES AND THEIR SYSTEMS. Organism as a whole
The division of labor between cells and their morphological differentiation leads to the union of cells into more complex units - BODIES that perform certain functions (kidneys, eyes or bones, for example). Several organs that together perform a certain function make up the organ system, digestive or musculoskeletal, for example. A complex of systems interconnected forms an ORGANISM. This becomes possible due to the emergence of an internal environment in animals during evolution, which is partially isolated from the external environment by a layer of external cells. Due to this, all the cells that make up the body are combined into a single organism. But this does not mean at all that the body’s connections with the environment are completely broken.
And muscle tissue. Epithelium is the cell layer that makes up the surface of the whole body, as well as the mucous membranes of the organs of the food and respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, glands, etc. The collection of epithelial cells of the body surface is called the “epidermis” and consists of five layers with different structures. The epithelium has a high ability to regenerate: in case of damage to the surface of the body, intensive division of epidermal cells begins.
Connective tissue is an auxiliary type of tissue. This is the only species that is present in the body in all four species: fibrous (ligaments), solid (bones), gel-like (cartilage) and liquid (lymph, blood, cerebrospinal and other fluids). Connective tissue accounts for 60-90% of the mass of all organs. It is very elastic due to the predominance of collagen and elastin fibers, joints suffer especially from its lack in the body.
Nerve tissue - the basis of the nervous system, which consists of nerve nodes, spinal cord and brain. The tissue is responsible for the overall coherence of organs. Nerve tissue cells are called "neurons" and work as "transmitters" of nerve impulses from external stimuli directly to organs or other cells.
Muscle tissue cells receive impulses from the nervous system and react with contraction, thereby causing the muscle to move. Tissue is responsible for the movement in the space of the body itself, as well as for the movement of organs inside the body to ensure normal functioning (heart, tongue, etc.). Muscle tissue consists of muscle fibers with the ability to change shape. The main functions of muscle tissue are motor, protective, heat transfer and facial expression.
The main functions of nerve tissue are the perception, processing and transmission of information. Neurons transmit an impulse to each other at the contact points of two neurocytes - synapses, with the help of neurotransmitters. The transmitting neuron releases a neurotransmitter into the synapse, and the receiving neuron picks it up and turns it into an electrical impulse. Nerve endings respond to various stimuli: mechanical, chemical, electrical and thermal. But all of them must be of a certain strength and act for quite a long time.
A distinctive property of nervous tissue is that new neurons do not form during the life of the body.
Related videos
In biology, tissue is a collection of cells that have the same structure and perform one function. Animal and plant cells differ from each other. The tissues formed by them are also different.

When the plants switched to a terrestrial way of life, a new stage in their evolution began. Organs began to form - parts of plants that perform different functions. According to the functions, cells began to specialize. So there were plant tissues.
The higher the step of the evolutionary ladder occupied by a particular plant, the more differentiated are its tissues. The most differentiated are the tissues of flowering plants.
All plant tissues can be divided into two groups: meristems (educational) and permanent tissues.
Meristems
Meristems are embryonic tissues. Their main task is to supply the plant with “building material” for its other tissues in the growth process. To accomplish this task, cells need to share, which they do throughout the life of the plant. The walls of these young cells are thin, the nuclei are large, and the vacuoles are small.
Distinguish between primary and secondary meristem.
The primary meristem forms a seed germ, and in an adult plant it remains at the tips of the roots and shoots, due to which these organs grow in length. The growth of roots and shoots in thickness, as well as the restoration of damaged organs provides a secondary meristem - pellogen and cambium.
Permanent tissue
Unlike meristem cells, cells of permanent tissues lost their ability to divide or even died. These tissues are divided into integumentary, conductive and basic.
The function of the integumentary tissue is to protect the plant. Of all its species, only the epidermis covering the green stems, leaves and parts of the flower is formed by living cells with thick walls. A cork covering roots, tubers, and wintering stems consists of dead cells that are saturated with a fat-like substance. Several layers of cork form a crust covering the lower part of tree trunks.
Conductive tissues conduct water, organic and mineral substances in different directions: from soil to root, from leaves to other organs. Conductive tissues are formed from blood vessels and sieve cells. Vessels are hollow cells with dead contents resembling tubes in shape. Sieve - living cells with sieve walls. Two types of cells form vascular fibrous bundles. They are surrounded by mechanical tissue of long cells with thick walls and dead contents. Its purpose is to strengthen the organs of the plant.
The main tissues are assimilation and storage. The cells of the assimilation tissue that forms the green stems and pulp of the leaves contain chlorophyll. The function of this tissue is gas exchange and photosynthesis.
Thin-walled cells of the storage tissue are filled with starch, protein, they contain vacuoles with cell juice. It is this kind of tissue that forms the parts of plants that are most often eaten - tubers, fruits, bulbs, root crops. It is contained in the seeds.
Related videos
Sources:
- Botany. Plant tissue in 2017
Modern women are mobile, they do not want to wait thirty minutes until the “miracle cream” is absorbed. And the mesoscooter worthily took a place on the dressing table of those who always want to look young and well-groomed.

The mesoscooter is similar to a roller, on the surface of which microneedles are made of titanium or an alloy of precious metals. When you roll the mesoscooter on the skin, a lot of micro punctures appear on it. This process should trigger skin repair processes.
Yes, indeed, the body has nowhere to go. He reacts to tingling as a wound and needs to protect and restore the skin. At the puncture site, a protective fibrous barrier is formed in the form of a scar. And since there are many such mini-wounds on the skin, a lot of scars also form, and scar tissue is denser. Due to this, the skin tightens and becomes denser.
This procedure has almost no recovery period and does not leave noticeable changes on the skin. Three types of mesoscooters are distinguished - home, cosmetic and medical. The mesoscooter for home use has small needles of 0.2-0.5 mm, completely not traumatic. Before using the mesoscooter, a special preparation can be applied to the skin for the effectiveness of the procedure. It can be a vitamin cocktail, hyaluronic acid concentrate, collagen.
Mesoroller has contraindications for the procedure. You can not use the roller for the skin in case of rosacea, pregnancy and breastfeeding, with endocrine pathologies, bleeding disorders, inflammatory conditions on the skin, a large number of moles. After using the mesoscooter, it is necessary to apply a cream with a sunscreen factor on the face before going outside. Its characteristic sound is due to the fact that the air collides with closed vocal cords.
Diaphragm structure
If we consider the diaphragm from a medical point of view, we can say that it has an irregular shape of two domes with a slight depression in the center for the heart, the so-called heart cavity.By its nature, the diaphragm is smooth muscle tissue, which, accordingly, consists of a tendon center and muscle part. The tendon center, in turn, is an accumulation of tendon and elastic fibers. The muscle part is usually divided into three components: the sternum, costal and lumbar. As you can see, the names correspond to the localization of the parts, which, respectively, are opposite the sternum, ribs and lower back.
It is believed that the lower borders of the diaphragm correspond to the places of attachment of the diaphragm to the sternum wall, the top of the right dome is at the level of the fourth rib, and the left - at the fifth intercostal space. From this it follows that the heart cavity is located at the level of attachment of the fifth ribs to the sternum.
What damage to the diaphragm leads to
I must say that damage to the diaphragm is very dangerous, as the esophagus and the main aorta of the human body pass through it. At its slightest relaxation, the process of digestion, respiration, and also the rhythm of the heart is disturbed.If the diaphragm, for whatever reason, remains undeveloped, slots remain in it. Instead, diaphragmatic hernias may soon form.
The strange thing is that the violation of the integrity of the membrane can be completely invisible. Only in rare cases, the violation can be accompanied by chest and heart pain, cough or dyspeptic symptoms.
As a treatment, surgery is prescribed, which can not always lead to a satisfactory result. But with successful treatment, the diaphragm completely restores its structure and takes on its original appearance.
Related videos
Related videos
The bodies of multicellular animals are composed of different types of cells that perform different functions in the body. Each type of cell includes not one cell, but many similar ones. Thus, one usually speaks of types of tissues (in this case, animals), and not types of cells.
The tissue is not only cells, but also the substance between these cells. This substance is secreted by tissue cells and is called intercellular. Tissues differ among themselves including the amount of intercellular substance. In some animal tissues there is a lot of it, in others - the cells are tightly adjacent to each other and there is almost no intercellular substance.
In this way, the cloth is a collection of cells having a similar structure and function, as well as the intercellular substance secreted by these cells.
Four main types of animal tissue are distinguished: integumentary, connective, muscle and nervous. Each type of fabric has its own subtypes. Therefore, they say, for example, not about connective tissue, but about connective tissue.
Coverslips
Cover tissues are also called epithelial.
The integumentary tissues line not only the surface of the body, but also the cavity of the internal organs. So the stomach, intestines, oral cavity, bladder, etc. are lined with integumentary tissues from the inside.
In the epithelial tissues there is almost no intercellular substance. Their cells are tightly adjacent to each other and form from one to several layers.
The main functions of the epithelium are protection, secretion, gas exchange, absorption, secretion.
it is expressed in the protection of deeper tissues of the animal from damage, temperature changes, ingress of harmful microorganisms. This function is performed by the skin.
the epithelium is characteristic of the intestines. Here, nutrients are absorbed into the blood with the help of intestinal villi.
the animal’s integumentary tissue is observed in the stomach, where its cells secrete mucus. Various glands are also present in the skin.
carries out the epithelium of the lungs, in some animals skin also takes part in gas exchange.
performs the epithelium of the excretory organs.
Connective tissue
Unlike integumentary tissues, there is a lot of intercellular substance in the connective tissue, in which relatively few cells are located.
Connective tissues form bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, adipose tissue, and blood. They perform supporting, protective, binding and other functions.
Blood belongs to the connective tissue, as it binds together various organs and organ systems. So the blood carries oxygen from the lungs to all cells of the body, and vice versa - carbon dioxide. From the digestive system, blood delivers nutrients to cells. Carries harmful substances into the excretory system.
Muscle tissue
The main function of muscle tissue is to ensure the movement of the animal. This occurs due to the alternate contraction and relaxation of the cells that make up the muscle tissue. The nervous tissue controls these processes.
Muscle tissue cells are elongated.
There are two main types of muscle tissue: striated and smooth. The first forms the skeletal muscles of the animal. Smooth muscles are part of the internal organs. Smooth muscle cells are elongated, but shorter than those of striated muscle tissue, in which the cells are long with many nuclei.
Neural tissue
Nerve tissue is made up of special cells - neurons. These cells have a body and processes, so the cell has a star shape. The processes are of two types: short and long. The processes transmit irritations from various organs of the body to the spinal cord and brain (which consist of nerve tissue). Here, the information is processed, after which excitation is transmitted from the nervous tissue to the organs, which is the body's response to irritation.
The function of the nervous tissue is the coordination of the work of various organs of a complex organism, its management, reaction to environmental influences, etc.
Lesson objectives
- Know the structure of the fabric.
- Be able to distinguish between types of tissue.
Lesson objectives
Based on knowledge of tissues, form anatomical and physiological concepts of human tissues; - applying comparison, analysis of various types of tissues to develop logical thinking, intellectual and creative abilities; - to improve the skills of quick and operational work with magnifying devices, with a textbook, mutual assistance, accuracy.
Key Terms
the cloth
Is a group of cells and intercellular substance, united by a common structure, function and origin
Histology
- tissue science
DURING THE CLASSES
Checking homework
1. What cells did we study in the course of botany and zoology?
Expected answer: Plant cells were studied in a botany course. A group of cells similar in structure and function is called tissue. In the course of zoology, we studied the animal cell and various types of tissues.
2. What types of plant tissue do you know?
(Coverslips, mechanical, basic, conductive, educational).
3. What types of animal tissue do you know?
(Integumentary tissue - skin, nerve tissue). Students find it difficult to answer, the question remains open.
The concept of "fabric" and their types
Human organism
- a complex holistic self-regulating and self-renewing system, consisting of a huge number of cells. At the cell level, all the most important processes occur; metabolism, growth, development and reproduction. Cells and non-cellular structures are combined into tissues, organs, organ systems and the whole organism.
Fabrics
- a collection of cells and non-cellular structures (non-cellular substances), similar in origin, structure and functions. Four main groups of tissues are distinguished: epithelial, muscular, connective and nervous. Picture 1.
Fig. 1. Groups of tissues.
On video 1 you can see human tissue
EPITELIAL TISSUE
Epithelial tissues are borderline, as they cover the body from the outside and line the inside of the hollow organs and walls of the body cavities. A special type of epithelial tissue - the iron epithelium - forms the majority of the glands (thyroid, sweat, liver, etc.), the cells of which produce one or another secret (Figure 2). Epithelial tissues have the following features: their cells are closely adjacent to each other, forming a layer, there are very few intercellular substances; cells have the ability to restore (regenerate).
Epithelial cells in shape can be flat, cylindrical, cubic. According to the number of epithelial layers, there are single-layer and multi-layer (Figure 3). Examples of epithelium: a single-layer flat lining the chest and abdominal cavities of the body; a multilayer flat forms the outer layer of the skin (epidermis); a single-layer cylindrical lining most of the intestinal tract; multilayer cylindrical - cavity of the upper respiratory tract); a single-layer cubic forms the tubules of the kidney nephrons. Epithelial tissue functions; protective, secretory, suction. 
Fig. 2. Glandular epithelial tissue

Fig. 3. A variety of layers of epithelium
MUSCLE
Muscle tissue causes all types of motor processes within the body, as well as the movement of the body and its parts in space. This is due to the special properties of muscle cells - excitability and contractility. All muscle cells contain the finest contractile fibrils - myofibrils, formed by linear protein molecules - actin and myosin. When they slide relative to each other, a change in the length of muscle cells occurs.
There are three types of muscle tissue: striated, smooth and cardiac. The striated (skeletal) muscle tissue is constructed of many multinucleated fiber-like cells 1-12 cm long, you can see it in Figure 4. The presence of myofibrils with light and dark areas that diffract light differently (when viewed under a microscope) gives the cell a characteristic transverse striation, which determined the name of this type of fabric. All skeletal muscles, muscles of the tongue, walls of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, upper part of the esophagus, facial, diaphragm are built from it. Features of striated muscle tissue: speed and randomness (i.e., the dependence of the reduction on the will, human desire), the consumption of large amounts of energy and oxygen, fatigue. 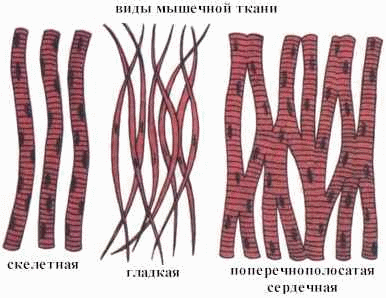
Fig. 4. Muscle tissue.
Cardiac tissue consists of transversely striated mononuclear muscle cells, but has other properties. The cells are not arranged in a parallel bundle, like skeletal ones, but branch, forming a single network. Due to the many cellular contacts, the incoming nerve impulse is transmitted from one cell to another, providing a simultaneous contraction and then relaxation of the heart muscle, which allows it to perform a pumping function.
Cells of smooth muscle tissue do not have transverse striation, they are fusiform, mononuclear, their length is about 0.1 mm. This type of tissue is involved in the formation of the walls of tube-shaped internal organs and blood vessels (digestive tract, uterus, bladder, blood and lymph vessels). Features of smooth muscle tissue: spontaneous and small force contractions, the ability to long tonic contraction, less fatigue, a small need for energy and oxygen.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Connective tissues (tissues of the internal environment) combine groups of tissues of mesodermal origin, very different in structure and function. Types of connective tissue: bone, cartilage, subcutaneous fatty tissue, ligaments, tendons, blood, lymph, etc. (Figures 5 and 6). A common characteristic feature of the structure of these tissues is the loose arrangement of cells separated from each other by a well-defined intercellular substance, which is formed by various fibers of a protein nature (collagen, elastic) and the main amorphous substance. 
Fig. 5. Connective tissue (Bone and Cartilage) 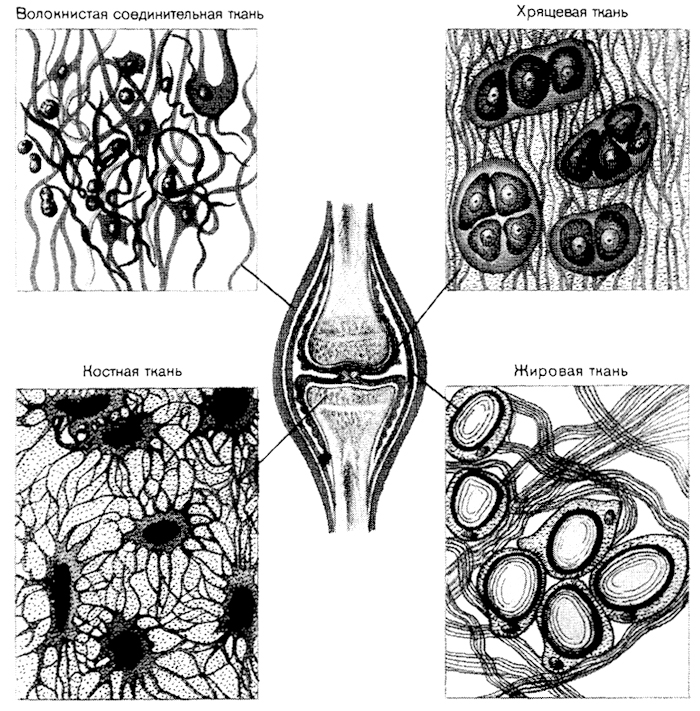
Fig. 6. Connective tissue (Fibrous and Fat)
Each type of connective tissue has a special structure of intercellular substance, and consequently, different functions associated with it. For example, salt crystals (mainly calcium salts) are located in the intercellular substance of the bone tissue, which give the bone tissue a special strength. Therefore, bone tissue performs a protective and supporting function.
Blood is a type of connective tissue in which the intercellular substance is liquid (plasma), due to which one of the main functions of the blood is transport (transfers gases, nutrients, hormones, end products of cell activity, etc.).
The intercellular substance of the loose fibrous connective tissue located in the interlayers between the organs, as well as connecting the skin with muscles, consists of an amorphous substance and elastic fibers freely located in different directions. Due to this structure of the intercellular substance, the skin is mobile. This fabric performs supporting, protective and nourishing functions.
Guys, watch the video “Microscopic structure of epithelial and connective cells. What can you say about what you’ve watched?
NERVOUS FABRIC
The nerve tissue from which the brain and spinal cord, nerve nodes and plexuses, peripheral nerves are built, performs the functions of perception, processing, storage and transmission of
formation coming from both the environment and the organs of the body itself. The activity of the nervous system provides the body's response to various stimuli, regulation and coordination of the work of all its organs.
The main properties of nerve cells - neurons that form the nervous tissue, are excitability and conductivity. Excitability is the ability of nerve tissue to become excited in response to irritation, and conduction is the ability to transmit excitation in the form of a nerve impulse to cage (nervous, muscle, glandular). Thanks to these properties of the nervous tissue, perception, conduction and formation of the body's response to the action of external and internal stimuli is carried out.
A nerve cell, or neuron, consists of a body and processes of two types (Fig. 7). The body of the neuron is represented by the nucleus and the surrounding area of \u200b\u200bthe cytoplasm. This is the metabolic center of a nerve cell; when it is destroyed, it dies. The bodies of neurons are located mainly in the brain and spinal cord, i.e., in the central nervous system (CNS), where their clusters form the gray matter of the brain. Accumulations of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system form nerve nodes, or ganglia. 
Fig. 7. Nerve tissue
Short, tree-branching processes extending from the body of a neuron are called dendrites. They perform the functions of perceiving irritation and transmitting excitation to the body of a neuron.
The video shows you a nerve cell
Lesson conclusions
- 1. Epithelial tissue. Cells are located tightly to each other, intercellular substance is not developed. They serve as a barrier, protection and secretory functions. Correspondingly found in the body: it is the surface of the skin, the mucous membrane of the internal organs, salivary glands, sweat.
- 2. Connective tissue. Cells are located relatively far apart, the properties of the tissue depend on the intercellular substance. If the intercellular substance is liquid, it is blood; if it is loose-fibrous, it is skin, and solid, it is bone. Accordingly, the functions - support, protection, transport of substances.
- 3. Muscle tissue. It is based on muscle fiber. Cells can be fusiform with a single core, this smooth muscle tissue is part of the walls of internal organs (stomach, esophagus, blood vessels, intestines).
- Transverse - striped, multi-core form the muscles of the body. We will talk about them while studying the muscles of the body of man .
- Cardiac striated tissue.
Control unit
Below are the drawings, think about what kind of fabric? 
Fig. 8. 
Fig. 9 
Fig. ten. 
Fig. eleven 
Fig. 12.
Homework
Correlate the fabrics under the numbers 1, 2, 3 and the structural features under the capital letters A, B, C and the functions under the letters a, b, c.
Relate the tissues, the features of the structure of tissues and functions.
I. Fabrics:
1) Epithelial;
2) Connective;
3) Muscular.
II. Features of the structure:
A) There are three types of fabric, the main feature of which is the ability to contract.
B) The cells are loose: the intercellular substance is well developed.
C) Cells lie tightly to each other in one or several rows, capable of rapid regeneration.
III. Tissue function.
a) Propulsion.
b) Protective, secretory.
c) Support, protection, transport.
Man is truly an amazing creature - every cell of our body, each of its components is a part of the universe. But do we know ourselves so well?
So, we bring to your attention some interesting facts about us and you ...
In Man, more than 10 to 14 degrees of cells.
It is 60% water. It is distributed unevenly:
so in the fatty tissues of water -20%,
in bones - 25%, in the liver -70%,
in muscles - 75%, in blood - 80%,
in the brain - 85% of the water of its weight.
The remaining 40% of the weight of the human body is distributed as follows:
proteins - 19%, fats - 15%, minerals - 5%, carbohydrates - 1%.
The body of an adult contains about 70 kg. oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen.
Calcium and phosphorus - about 2 kg.
Potassium, sulfur, sodium, chlorine - there are several tens of grams.
Iron in a person is only about 6 grams, but it plays an extremely important role when entering hemoglobin.
The total length of human blood vessels is approximately 100,000 km.
At rest, the blood is distributed as follows:
25% in the muscles
25% in the kidneys
15% in the vessels of the intestinal wall,
10% in the liver,
8% in the brain,
4% in coronary vessels of the heart,
13% in the vessels of the lungs and other organs
Bibliography
1. Lesson on the topic "General review of the human body" I. Matveeva, biology teacher, Novocheboksarsk, secondary school No. 17.
2. A series of lessons on the topic "General review of the human body" Koval L.N., chemistry teacher, Chelyabinsk, secondary school No. 107.
3. Matyash N.Yu., Shabatura N.N. Biology, 9 cells - K .: Genesa, 2009
4. D.V. Kolesov, R.D. Mash, I.N. Belyaev. "Biology. Person". Textbook. 8 cl. . - M.: Bustard, 2002.
5. G. M. Murtazin "Active forms and methods of teaching biology: Man and his health": Prince. for the teacher: From work experience. - M.: Education, 2008.
6. Zverev I. D. "A book for reading on the anatomy, physiology and human hygiene." - M .: Education 2003.
Edited and sent by Borisenko I.N.
Worked on the lesson:
Matveeva I.
Koval L.N.
Borisenko I.N.
You can ask a question about modern education, express an idea or solve an urgent problem at Educational forum where internationally gathers educational advice for fresh thoughts and actions. By creating a blog You will not only improve your status as a competent teacher, but also make a significant contribution to the development of the school of the future. Education Leaders Guild opens the door for specialists of the highest rank and invites to cooperation in the direction of creating the best schools in the world.
Subjects\u003e Biology\u003e Biology Grade 8In multicellular animals, cells make up tissues. Tissue is a group of cells similar in structure and function and intercellular substance secreted by these cells.
In the body of animals there are the following types of tissues: epithelial (integumentary), connective, muscle, and nervous.
Epithelial tissue, or epithelium, form. covers of animals, line the cavity of the body and internal organs (Fig. 19. 1-3). Different epithelial tissues consist of one or several layers of tight-fitting cells and almost do not contain intercellular substance. In the body of an animal, they perform protective, secretory, gas exchange, suction and some other functions. Covers protect the body of the animal from shock, damage, overheating, hypothermia.
Nutrients are absorbed into the intestinal epithelium. The epithelium of the stomach can secrete mucus. The epithelium lining the respiratory system is involved in gas exchange; the epithelium of the organs of excretion is involved in the removal of harmful metabolic products from the body.
In the skin covering the body of vertebrate animals, there are glands. The sebaceous glands in birds and mammals secrete a greasy secret that lubricates feathers and wool, giving them elasticity and preventing them from getting wet. V animals have sweat, odorous and mammary glands.
Connective tissue consist of a relatively small number of cells scattered in the mass of intercellular substance (Fig. 19. 4, 5), and perform supporting, supporting, protective and binding functions. These tissues consist of cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments.

Fig. 19. Structural diagrams of various tissues and animal cells: 1,2,3 - epithelial tissues: 4,5 - connective tissues; 6.7 - muscle tissue; 8 - cells of the nervous tissue
The connective tissue, which is part of the skeleton, supports the body, creates its support, protects the internal organs. In the adipose connective tissue, reserve nutrients are deposited in the form of fat. A kind of connective tissue is blood. It provides an internal connection between organs: it transfers oxygen from the lungs to all organs and tissues, and carbon dioxide from them to the lungs. Blood delivers nutrients from the intestines to all organs, and harmful metabolic products to the organs of excretion.
Muscle tissue consist of elongated cells that take irritation from the nervous system and respond to it with contraction (Fig. 19, 6, 7). Due to the contraction and relaxation of skeletal muscles, animals move and move individual parts of their body. Muscles shape the body, support, protect internal organs.
Internal organs have smooth muscle tissue, consisting of elongated cells with rod-shaped nuclei. The striated muscle tissue in mammals forms skeletal muscle. Its muscle fibers are long, multi-core, have a well-marked transverse striation.
Neural tissue forms the nervous system, which consists of nerve cells - neurons whose bodies are star-shaped, long and short processes (Fig. 19. 8). Neurons perceive irritation and transmit excitement to muscles, skin, other tissues, organs. Nerve tissue provides a coordinated body function.
In multicellular animals, groups of cells of the same structure and function form tissues. Animals have epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve tissue.
Material Exercises
- What is tissue in animals?
- What types of tissues do multicellular animals have?
- What are the characteristics of epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue? What functions does each of these tissues perform in animals?

